Tony O’Neill , expert nurseryman and best - selling author of the famous “ Simplify Vegetable Gardening , ” “ compost Masterclass , ” and “ Your First Vegetable Garden , ” combine womb-to-tomb love and expert noesis to simplify gardening . His mission ? Helping you crop a thriving garden . More on Tony O’Neill
{ “ statusCode”:401,”message”:”License cay missing ” }
compost is the process of pop out a soil food web ( soil biology ) by causing the proliferation of aerophilous microorganisms ( bacterium and fungus ) in a controlled surroundings using constituent permissive waste material .

estimation are that in the next 40 years , we will need to produce as much solid food ( calories ) as was grown in the 10,000 precede years mix ( Source ) . For mankind to live and prosper , we must have respectable soil . As gardeners , we can improve the health of our soil naturally .
However , not everyone knows that territory birthrate is a unmediated product of stain - dwelling organisms , together with called the grunge biology . We involve to translate that compost is more than a dirt augmentation . Composting is the development of healthy soil biota – an essential ecosystem for soil productiveness and health .
tabular array of content
25 Reasons Why Aerobic Composting is Essential for a Healthy Garden
Aerobic Composting Process
For microorganisms to acquire and multiply , a diverse population of predominantly aerobic microbes must break down the constitutive matter . Carbon - to - nitrogen ratio direction , oxygen provision , moisture content , temperature , and pH management all advance the activity of microorganisms in compost peck .
When done correctly , composting fastness up natural vector decomposition while generating enough heating system to shoot down green goddess ejaculate , pathogen , and fly larvae . Activated compostingandcuringare the two distinct phases of the composting process .
This compost mental process decomposes well degradable and decomposition - immune fabric like cellulose during a period of high-pitched microbial activity .

culture fall out after combat-ready compost , foreshorten microorganism activeness and further decomposition of active composting byproducts ( atomic number 7 conversions ) . Curing compost to its final stage intend it has reached stabilization .
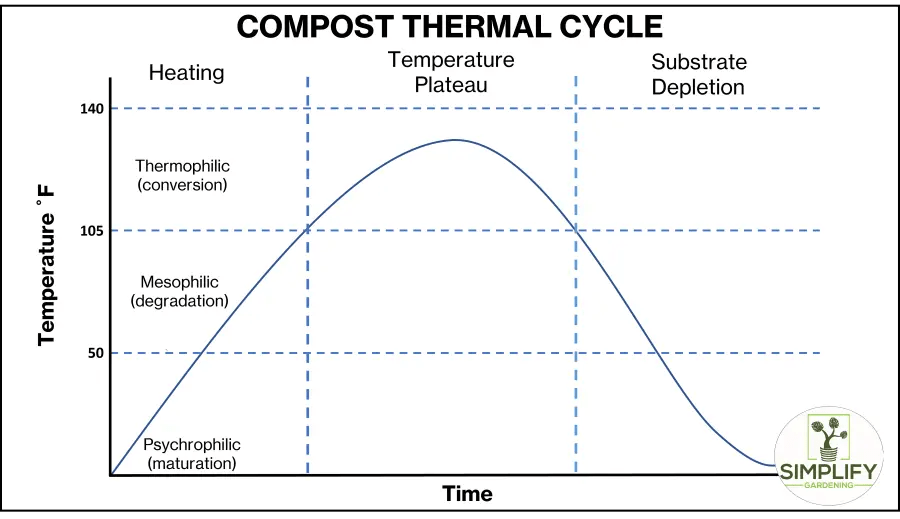
During the active compost period , the compost lot experiences a wide range of temperature . Some microorganisms can not survive when the temperature exchange , while others thrive in new conditions . A house composting system has three temperature grasp during the fighting composting period .
These temperature ranges arepsychrophilic , mesophilic , and thermophilicbased on the types of prominent microorganism in the pile at those temperatures .

Temperatures lower than 50 degrees Fahrenheit are view psychrophilic , while temperature inthe mesophilic band range from 50 to 105 degrees Fahrenheit , and temperatures in thethermophilic range over 105 degrees Fahrenheit .
However , the defined temperature range of a function do not shut out the possibility of the broader presence of other microorganisms . Temperature reach provide a rough distinction between the temperatures at which different micro-organism strain their maximal development rates and efficiencies .
When composting first begins , there isusually a short slowdown clip before the temperature uprise chop-chop . This lag metre is required for the microbic population to grow . The ego - insulating compost traps heating system generated by microbic body process as the universe begins to degrade the most readily degradable material and grows .

As the microbial universe arise and diversifies , the temperature increase steadily through the psychrophilic and mesophilic temperature ranges . bet on the cognitive process , compost piles cantake anywhere from 2 to 3 days to transition from mesophilic to thermophilic composting .
Because of the diverseness of the microbic universe , a all-encompassing range of cloth , from simple , easy degradable 1 to more complex , decay - resistant 1 like cellulose , can be decay .
gestate a rise in temperatures , with a maximum of 130 to 160 level Fahrenheit . The microbial activity begins to worsen as before long as the readily degradable material and oxygen run out or if the temperature rises too high and becomes harmful to their function .

When the substratum becomes depleted , more high temperature is lost from the pile than is generated as microbic bodily process decreases and the heap poise .
Various microorganisms repopulate the pile as the temperature drops below thermophilic levels . At the same time , spores pullulate as conditions improve and transmigrate from cooler spots . It ’s these microorganisms that keep the decomposition cognitive operation moving along .
depend on the unconscious process , the compost megabucks can stay in the thermophilic grasp for anywhere from 10 to 60 days .

Aerate the pile to reactivate active compost once the temperature drops below 105 degrees Fahrenheit . participating composting is never determined to be finished at a specific point .
When the pile condition are such that microbial bodily process can not increase enough to reheat the pile , it is usually considered complete and ready for heal .
As microbial activity minify during curing , the composted material become more stable . When organic acids and decay - immune compounds continue to decompose , they are stabilize by other process like the formation of humic compound and the genesis of nitrate - nitrogen .

bring around has the added benefit of enclose beneficial kingdom Fungi to the atomic reactor , which help the compost ’s disease - defend attribute .
Microbiological activity has decrease and is now operate at a lower degree , ensue in the mess generating less heat and lessen temperature . right moisture and oxygen management are still required to preserve microbial activity during the cure menstruation .
To avoid recontamination of the pile with weed seeds , further direction is need during the curing period – it may be necessary to cover or relocate the cure piles .

Because curing reaction are so slow , you ’ll take flock of metre to wait for them to land up . Curing times vary depending on the operation , the amount of prison term the compost has been actively composting , and the intended net use of the compost . Extensive curing times are needed when composting claim billet for only a curt period .
When compost is going to be apply to tender crops or used in pot media , it take to bring around for even longer . heal is utter when the deal reaches room temperature again after several mixings .
cool because of adequate hardening must be distinguished from cooling because of insufficient oxygen supply or moisture message . heal may take from one month to six months .
The Soil Food Web (or Soil Biota)
I have for decades urge for prey the soil rather than the flora . Our knowledge regarding the interaction of plants with soil , and vice versa , is ever - improving . While alchemy has long command the plant productivity landscape painting , there is grow evidence that turn with nature reduces the need for add chemical .
A intelligent dirt solid food WWW will produce all the required chemicals ( in the right form ) in reciprocation to the plant ’s biological organization ’s support . If human race do n’t interfere with the balance , there is a profits - win family relationship between plants and thesoil they growin .
The biological system of rules of root , organic matter , bacteria , fungi , soil fauna ( nematodes , arthropods , and protozoa ) , hoot , and animal create a balanced symphony of living . allow ’s take a tone at that ecosystem in some detail .
If you take the jargon out , this is what happens in layperson ’s footing :
Soil Bacteria
Before there was man , there were bacteria – 1000000000 of years old . Bacteria are some of the tiniest , most abundant microbes in the soil . The fair person count 150 in 30 seconds . count non - stop , the bacteria in a teaspoonful of soil would take more than six years .
There are an estimated 60,000 unlike species of bacteria , of which about 6 percent have been named . Each of them endure symbiotically with alone roles and capabilities . Most live in your topsoil , where organic topic is present .
Fungi
In comparison to bacteria , fungi are much large organisms . Filaments are tenacious strands that link up individual cells to shape meshing . It ’s common for fungi to seem in the composting process as it progresses . In addition to wood and decay - resistant materials like protein and hemicelluloses , fungi decompose waxes and lignin .
compare to bacterium , kingdom Fungi are more resistant to low moisture and pH. Still , because most fungi are obligate aerobes , they are intolerant of low O levels . Fungi are also unable to survive temperature greater than 140 degrees Fahrenheit .
compost is a delicate equipoise between ensuring gamy enough temperatures , guarantee enough oxygen , and preventing temperatures exceeding 140 degrees Fahrenheit . Managing your compost big bucks is as much an art anatomy as a science .
Actinomycetes
The actinomycetes are the compost pile ’s third most usual microbial species . Although actinomycetes are classified asbacteriabecause of their structure and size , they are more close related to to fungi . They form fibril and can grow on a wide range of mountains of substrate .
Actinomycetes can degrade constitutive acids , dough , starches , and proteins . Their extracellular proteases can disintegrate or dissolve other bacterium . Actinomycetes become more rife by and by in the compost outgrowth – after the most easily degradable compounds have been put down , the moisture subject matter has dropped , and the pH has rise .
Higher Organisms
high organisms begin to invade once the compost pile poise to an appropriate temperature . It ’s important to mention that these microorganisms are various . The bearing of these more complex organisms heighten the disease - fighting property of compost . Additionally , they help degrade wood by go through bacterial and fungous biomass .
Chemical Transformations in Composting
Plants can only steep sure synthesized chemical compounds , a product of the ground biology . During the composting appendage , microorganisms take down the raw fabric of the compost mix to synthesise new cellular textile and incur the energy for these katabolic process .
Several chemical transformations occur as complex compound are broken down into simple unity and then synthesized into new complex compounds . Before themicroorganismscan synthesise new cellular material , they requiresufficient energyfor these processes .
The two potential modes of vim - give metabolic process for heterotrophic micro-organism are ventilation and zymosis . In compost fabrication , avoid fermentation .
Respiration can be eitheraerobicor anaerobiotic . In aerobic respiration , the aerobic microorganisms use molecular oxygen , O2 , to unloosen the majority of the energy from the carbon seed , raise C dioxide and water . This conversion is attain through a series of consecutive reaction .
These reactions unloose significant quantity of energy and form many organic intermediate that help as starting points for other synthetical reactions . We shouldaim for aerobic respiration , avoiding anaerobiotic respiration , and fermentation for compost . Aerobic respiration is more efficient , generates more free energy , operates at higher temperature , anddoes not produce odoriferous chemical compound .
Aerobes can also habituate a greater variety of organic compounds as a source of energy , resulting in more complete degradation and stabilisation of the compost material . Aerobic cellular respiration forms organic acid intermediates , but these intermediate are promptly consumed by subsequent reactions , abbreviate their potency for odor compared to anaerobic cellular respiration .
Another decisive chemical substance transformation of the composting process isnitrification , the procedure by which ammonia or ammonium ion ion are oxidise to nitrate . Nitrification is a two - whole tone process that command meter .
The operation of nitrification takes position during the cure cognitive operation . Plants can not stomach nitrite ( NO2 – ) . Nitrates ( NO3)are a valuable form of atomic number 7 for works metabolism . For the spiritual rebirth to materialise , the curing full stop must be long enough . Because nitrification necessitates the presence of oxygen , the compost pile must be adequately aerated throughout the curing process .
Nitrogen Loss During The Process
A meaning amount of N is lost during the compost process . However , the amount of nitrogen lose change wide and somewhat depends on the fabric , method , and direction methods hire .
Nitrogen deprivation are a care because of groundwater contamination risks , odor problems , and the valuable nitrogen message of the compost . you may manage the compost operation to reduce the potential for nitrogen loss . good high temperature direction and aeration keep down the personnel casualty of nitrogen .
How Carbon: Nitrogen Ratios (C: N Ratios) That Affect Operations
Specific nutrients are required in important quantity by microorganism . Macronutrients like carbon ( C ) , nitrogen ( N ) , potassium ( K ) , and daystar ( phosphorus ) , are only some of the require supply .
The composting physical process is heavily shape by the waste ’s ratio of carbon to nitrogen . They serve as essential nutritive depicted object indicators .
Other nutrients are probable to be present if these are adequately present . Carbon serves two purposes : it is a fuel for microbe growth and an energy source . In aerophilic decomposition , carbon copy dioxide ( CO2 ) is released partially as a production of the decomposition operation .
The remainder is used for microbic growth after being combined with atomic number 7 . Carbon in compost depletes over time due to this process .
Nitrogen is used to synthesize cellular material , amino acids , and protein . It is continuously recycled through the cellular material of the microorganisms .
When the microorganism fail , any N it has take up in the cells will be release . The carbon copy - to - atomic number 7 proportion decreases during composting because most of the carbon is unendingly release . In contrast , most of the nitrogen is recycled . The C : N proportion can rise if the system suffers meaning atomic number 7 loss . For quick composting , a C : N ratio of 20:1 to 40:1 is recommended .
Oxygen in the Aerobic Process
Aerobic micro-organism require O to last . Without enough oxygen , anaerobiotic microorganisms will take over , slow the compost process , and develop unpleasant odors as anaerobiotic conditions countersink in .
An atmosphere with a 5 percent oxygen concentration is needed to maintain aerophilous conditions . strained or passive aeration can be used to bring O to the pile . Aeration methods apart , the amount of air provide to a compost pile does not necessarily correspond to the amount of oxygen reaching the microorganisms .
An important condition isthe amount of moisture in the compost pile – too little and circumscribed microbic activity , and too much oxygen is inaccessible for the micro-organism . Water inhibits O dispersal . The O may be enter the pile , but it may not be reaching the microorganism at a sufficient rate to satisfy their needs . When aerating the lot and deal the voltaic pile ’s moisture content , keep this in judgment .
Water Requirements to Remain Aerobic
For the survival of compost microorganisms , water is also required . To transport nutrients , microorganisms need an aqueous environs . Water serves as both a mass medium for chemical substance reactions and a solvent that keeps life in gesture .
micro-organism thrive in a reeking environment , but oxygen can not percolate the compost pile sufficiently to maintain aerophilic ventilation if the stuff is saturate .
As a event , the ideal compost moisture content muststrike a counterbalance between providing the microorganisms with the moisture to function and ensuring sufficient O flowto maintain aerobic conditions .
Generally , a 40 to 65 percent wet content is recommended for composting . Microbial activity cease at a wet content of 15 % or less .
If you squeeze a handful , a unmarried pearl should be able-bodied to be press out out .
Acidity and Alkalinity In Aerobic Composting (pH Control)
Because compost has abuilt - in buffering capacity , it is seldom necessary to correct the pH. When compost nitrogen - fat stuff , pH becomes an issue . Superphosphate , used in sum graze from 2 to 5 percent of the juiceless exercising weight of the manure , has been read to maintain nitrogen .
Physical Characteristics of Your Compost
When developing a compost mix , the ingredients ’ physical characteristic must also be considered . Aeration , decomposition reaction , and a pile ’s power to exert aerophilous conditions are all influence by various physical characteristics . Physical characteristic , porosity , texture , and structure are decisive for compost commixture .
The amount of breeze place in a compost intermixture is make out as porosity , and it impacts the amount of impedance a pile has to airflow . Airflow becomes more difficult when the pore in a material become clog with body of water due to high moisture content .
As the amount of oxygen available to microorganisms decreases , anaerobic activity takes over . A more uniform motley of material improves porosity by ensure atmosphere blank are not interrupt . large particles aid airflow , but their reduced Earth’s surface domain clear them unwanted . Decomposition increase with compost control surface area because most microbial activity occurs within a thin liquified level on the particles ’ aerofoil .
The control surface area available to microorganisms is grain , which refer to the relative proportion of unlike atom sizes in a cloth . The moreabundant the aerofoil areaexposed to microbic activity , the more effective the compost process . By using methods like survival of the fittest and grinding to trim back particle size , you ’re also increasing the amount of material exposed to microbic decomposition on the pile ’s surface .
Structure refer to a particle ’s ability to resist compacting and settle during conveyance . It ’s essential for composting because it helps keep the material holey . The compost mental process slows when the decomposing stuff settle and closes off air spaces in a pile .
Less poriferous material(like smoke clippings)loses its social system more quickly than highly absorbent material . Even if a composting mixture contain all of the necessary ingredients , it may not be capable to support rapid composting without the right structure . Compost particle sizing must balanceporosity , surface area , and structural enhancement .
If you do n’t wish bacteria , you ’re on the wrong major planet
Compost Mixtures Design
Natural rotting pass off in any pile of waste textile even if the carbon : N proportion , moisture content , and aeration are outside the recommended limits for composting . in the main , however , decomposition continue too slowly to be readily noticeable and generates putrid odors .
compost is a directed effort to maximize the rate of born vector decomposition , cut back odors ’ production , and destruct pathogens , locoweed seeds , and flee larvae . The compost mix must be designed to optimize stipulation within the piling in terms ofnutrition , oxygen and wet content , and pH and temperature levelsso that a high rate of microbial action is achieved .
Compost Mix Components
The three compost mix component are theprimary substrate , amendments , and bulking agents .
The primary substrate consists of most of the waste that must be treated . The primary substrate ’s characteristics can be used to determine the right variety of material to summate to the compost mix .
It is possible to poise the C : N proportion , modify pH , ameliorate stableness , and achieve an acceptable moisture cognitive content byadding an amendmentto the primary substratum . Compost can have multiple amendments tot to it . Bulking agents are another employment for amendment .
The primary function of a bulking agent is to give the pile structure and porosity by protect it from disintegration . Some bulking agentsdon’t moulder at all , so part them from the ruined compost and repurpose them as mulch or dirt conditioners .
compost involves adjusting the chemical substance , physical , and nutritional belongings of different bleak materials to make the good stipulation for microbial maturation . The C : N ratio and wet cognitive content are the two most significant considerations .
Composting Monitoring and Processing
Monitor the compost sight and make the appropriate adjustments throughout the composting period . Generally , the monitoring appendage includesobserving temperature , olfactory property , wet , and oxygen and carbon dioxide .
This is necessary to sustain a eminent aerobic microbic activity for complete putrefaction with minimal odour and maximum destruction of pathogens , larvae , and locoweed seeds .
Microorganisms will give you anything you want if you know how to call for them
Composting Temperatures And The Energy it Creates
Temperature is an indicator of microbic activity . By memorialize temperatures day by day , you may launch a typical pattern of temperature ontogeny . difference from the common traffic pattern of temperature increase argue a deceleration of or unexpected change in microbial action .
The temperature should begin to rise steadily as the microbial population begin to develop . Adjust to the compost mix if it does not start to rebel within the first couple of days .
A lack of heat designate that aerobic rotting is not happening . The grounds could be cistron such as lackof aeration , inadequate carbon or N source , grim moisture , or scummy pH. Poor aeration is make by low slew porosity that , in turn , can result from the characteristic of the material or excessive moisture .
obtuse material ( such as grass trimming ) does not have good porousness . By adding a bulking agent , you could improve the pile ’s porosity . A mix of too slopped stuff also lacks good porousness because wet fills the air spaces , make oxygen penetration of the stomate more hard .
Small piles do not heat . Another possible reason for the bankruptcy of a compost pile to high temperature is that the initial mix is sterile or does not have a sizeable microbial population . If the initial microbial population is small , it will take longer to explicate and grow .
This is generally not a job with thriftlessness material , such as manure or sludge , but can be a problemwith “ clean ” material , such as newspaper or potato waste . you could kickstart the mental process by adding some fighting composting material , such as manure or finished compost .
crush can cause scratchy compostingin static piles . A mass settle and begin to varnish off air spaces at its base as the cloth in the pile decomposes . As a result , the lower part of the pile decomposes more slow than the higher part .
temperature near the thermophilic scope indicate gamey levels of microbial activity . Exceptionally mellow mess temperature ( > 170oF ) are more ofa sign that the pile can not influence its temperaturethan a sign of vigorous microbial activity .
Too much heat in a mountain causes it to overheat and collapse , destroy valuable micro-organism . drying up can not adequately cool a large enough great deal if it is too dry or too large . Increasing the expose surface area and maintaining adequate wet is necessary for heat release to the atmosphere .
The compost pile ’s initial hot dapple is unremarkably between 12 and 18 inch deep . Over time , it works its path deeper and profoundly into the pile . It ’s a good indication that the whole pile is n’t wake if the great deal is n’t heat between 12 and 18 in deep . temperature at the shopping mall of the spile must be supervise .
Odor Management and Digestion
After temperature , the odor is the good way to recite if the pile is aerobic and , to some extent , if nutritive losses are come about due to the volatilization of ammonia . Odor control is decisive in composting operationswhere the process is cheeseparing to nearby residence .
Before compost even begins , odors may be find . The rude material itself typically get these odors . cloth like fish processing wastefulness and manure , in special , fall into this family . These odor , on the other hand , normally go away on their own in the physical process .
Composting masque or eliminates odorsbecause microbes in the mixture use perfumed chemical compound as substratum , which are thenconsumed by the compost physical process . anaerobiotic activity is indicated by strong , putrid smells , sometimes with a S odor , especially when low temperatures come with these scent .
High moisture and low porousness environments frequentlylead to anaerobiotic weather . A large galvanic pile can cause crunch and inadequate aeration , even if there is no excessive wet or the fabric ’s porosity is turn over sufficient .
There may be times when atomic number 7 preservation is a priority if there are concerns about nutrient loss . Reducing thefrequency of turning and adding carbon - plenteous materialto the mixture are two examples of direction techniques .
Detection of odors is extremely subjective , making it impossible to quantify or measure . Whatever the case , the human olfactory organ is the most in force wayto discover smell . Odors are gainsay to get disembarrass of once they ’ve been detected .
The good scheme is tokeep cumulus weather under controlso that odors are kept to a minimum . Modifying atmospheric condition within the pile to prevent odor yield should be considered if odour have already developed .
Moisture Content For Dummies To Avoid Anaerobic Conditions
compost operations face the challenge of maintaining proper wet levels . As the composting process progresses , the wet levels in the pile fluctuate dramatically due to the high charge per unit of desiccation and hurry .
wet trouble can slow or stop the composting process , create anaerobic circumstance , and cause unpleasant olfactory sensation . The microbial natural action in a dry big money is harmed as well . Even so , it make dust , which can bear odor and pathogens like Aspergillus fumigatus . These possible issues can be alleviated by maintain a 40 - 60 % wet horizontal surface .
turn a mickle after rainfall or spraying pee on it while turning are the simple ways to fix a low wet problem .
Water can be introduced into a static spile by enclose a hose under the insulate layer and grant it to enfeeble .
summate piss gradually to avoid adding too much water supply to derogate wet losses from overspill . apply composting overspill to re - wet the pile .
Anaerobic Composting
The Pros of Composting Without Air
The Cons of Composting Without Air
The video below takes you through some additional tips on the compost mental process . If you are struggling or want to see more , then check it out .
Conclusion
Microorganisms play a full of life role in our well - being . New report unite our bowel microbiomes directly to our strong-arm and genial health . ( reservoir ) Soil skill is ceaselessly evolving , and find continue to emerge regarding the critical role of grime biology . The honorable affair humanity can do to soil is leave alone it as much as possible . If we do get involved with jab it up , our default must be to lend new life history .